Ever experienced pain, discomfort, or difficulty while attempting to swallow? This condition is known as dysphagia. Dysphagia is highly common–around 13.5% of the population experiences it at some time–and it is caused by a variety of different medical conditions and diseases.
There are two main types of dysphagia: oropharyngeal and esophageal.
Oropharyngeal dysphagia is associated with the muscles of the mouth and upper throat. When muscles are weakened due to neurological and nervous system disorders, the act of swallowing may become difficult. This can also feel like a numbness of the throat, resulting in an inability to “feel” food. Multiple sclerosis, a stroke, Parkinson’s, and other brain disorders are associated with oropharyngeal symptoms.
Esophageal dysphagia is usually associated with a physical narrowing of the esophagus or motility issues of the esophagus and upper stomach. Some muscular conditions, such as muscle spasms, throat cancer, or diverticulum, can make it difficult to fully swallow food, resulting in discomfort. Physical blockages related to benign/cancerous growth or strictures may cause esophageal dysphagia.
Esophageal dysphagia is also a frequent symptom of gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), or chronic acid reflux. GERD is a result of dysfunction of the esophageal sphincter, a muscle in the esophagus. Normally, when you swallow, the esophageal sphincter muscle relaxes to allow food and liquid to enter your stomach. In GERD, the muscle relaxes abnormally or weakens, allowing stomach acid to enter the esophagus. This results in chronic discomfort, heartburn, chest pain, regurgitation, nausea, and dysphagia. In the long-term, GERD can lead to scarring and Barrett’s Esophagus, which is an abnormal change in the lining of the esophagus which can increase your risk for esophageal cancer.
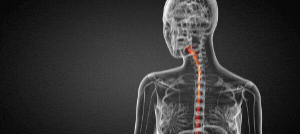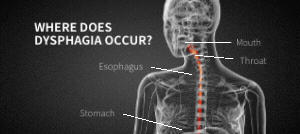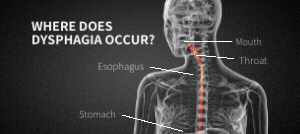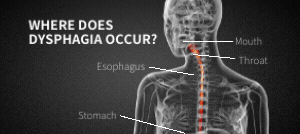
While dysphagia is most common in older populations, it can really happen to anyone. Dysphagia is almost always a symptom of another underlying condition. If you experience severe symptoms of dysphagia, seek immediate medical assistance.
If you experience dysphagia as a symptom of GERD, consider consulting a gastroenterologist. There are ways you can address symptoms of GERD to reduce severity and chronic symptoms. Some risk factors of GERD include obesity, hiatal hernia, pregnancy, smoking, asthma, diabetes, overeating, and connective tissue disorders, such as scleroderma. To learn more about heartburn, acid reflux, and GERD, click here. If you have been diagnosed with GERD and wish to manage symptoms through dietary choices, read our blog here.
If you are suffering from chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease, the experienced team at Gastroenterology Health Partners is here for you. Our clinicians have a passion for seeking out and refining new treatments and advanced solutions for those suffering from disorders of the digestive system. For more information or to schedule a gastroenterological medical evaluation, contact a Gastro Health Partners location near you.


